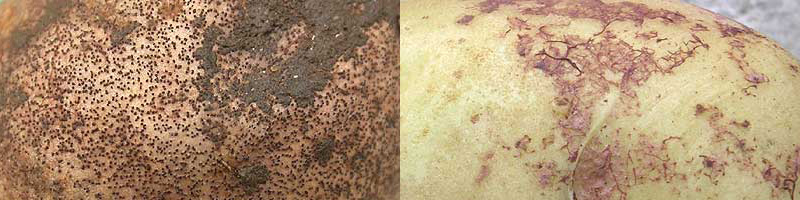
Rhizoctonia crocorum
(Violet root rot)
- Causal agent and transmission
Violet root rot is caused by a fungus, Rhizoctonia crocorum, and is responsible for rare but spectacular damage to potato tubers.
This fungus is a saprophyte and lives in the soil in the form of sclerotia that can survive for several years. Its development is favoured by humidity and relatively high temperatures. It is capable of developing on a large number of crops (alfalfa, beetroot, carrot, chicory etc.).
- Significance
The occurrence of violet root rot is rare and sporadic. As its incidence on yield is usually limited, no specific control measures are generally required.